Silicon steel mother coils are a fundamental raw material in the electrical manufacturing world. Known for their unique magnetic properties and low core loss, they are essential for producing transformers, motors, and generators. But what exactly are these coils? How are they manufactured, and why are they critical in today’s power-hungry world?
In this article, we’ll explore the definition, manufacturing process, classification, properties, applications, and quality standards of silicon steel mother coils, complete with a comparison table to help you understand their advantages.
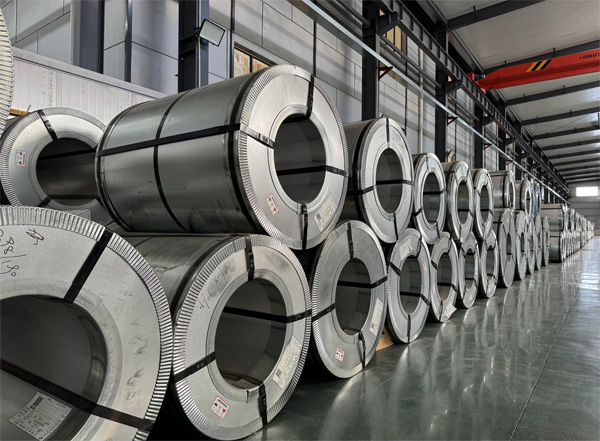
Silicon steel mother coils are large rolled sheets of silicon steel (also called electrical steel) in coil form, typically produced by steel mills before being slit into smaller coils or sheets for end-use manufacturing.
Silicon steel is an iron-silicon alloy, usually containing 2%–4.5% silicon. The addition of silicon improves electrical resistivity, reduces magnetic losses, and enhances magnetic permeability—making it ideal for electromagnetic applications.
The term “mother coil” refers to the primary, wide coil that comes straight from the rolling mill before further processing.
The manufacturing process generally involves:

| Type | Grain Orientation | Silicon Content | Key Features | Main Applications |
| Grain-Oriented (GO) | Grain structure aligned to rolling direction | ~3% | Low core loss in one direction, high permeability | Power transformers, distribution transformers |
| Non-Grain-Oriented (NGO) | Random grain orientation | 2%–4% | Uniform magnetic properties in all directions | Motors, generators, alternators |
| High-Silicon | >4% | Very high resistivity | Reduced eddy current loss | High-frequency transformers |
| Thin-Gauge NGO | <0.35 mm thickness | 2%–4% | Lower hysteresis loss | High-speed motors, electric vehicle motors |
Energy loss in transformers and motors directly affects global electricity consumption. Using high-quality silicon steel mother coils can improve device efficiency by up to 5%, significantly reducing CO₂ emissions and operational costs.
| Standard | Common Grades | Notes |
| ASTM A876 | M15, M19, M27, M36 | NGO grades for motors and generators |
| JIS C2552 | 35A300, 50A470 | Low-loss electrical steel for transformers |
| EN 10106 | 30QG100, 23QG90 | GO grades for power applications |
| GB/T 2521 | 30W130, 50W470 | Chinese standard for silicon steel |
Silicon steel mother coils are the starting point for producing the cores of electrical devices that power our modern world. Their magnetic efficiency, low core loss, and adaptability make them irreplaceable in the manufacturing of transformers, motors, and generators.
By selecting the right grade, thickness, and coating, manufacturers can ensure better energy efficiency, longer equipment life, and reduced environmental impact.
 +86-523 8891 6699
+86-523 8891 6699  +86-523 8891 8266
+86-523 8891 8266  info@tl-core.com
info@tl-core.com  No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China
No.1, Third Industrial Park, Liangxu Street, Taizhou City, Jiangsu, China 

 English
English Español
Español Türk
Türk 中文简体
中文简体